Octopi is a Linux distribution that gives you the ability to control and view most 3D printers from a webpage. There are options to create a video time lapse, temp control, temp monitoring, bed temp control, print storage, view Gcode as the print is happening and a terminal to view and send commands. The printer also has Cura 15.01 baked in so you can slice your files on the Raspbery Pi. Although that option is available, It is slow and an outdated version of Cura so I typically upload the Gcode files that I’ve already sliced from my computer.There are install instructions for Mac and Windows, however this distribution was designed to operate on a Raspberry Pi.
Installation
For a typical install you will need hardware below:
- Raspberry Pi (I use model 3) $35
- A camera (I use a Pi camera from eBay $5)
- 32GB micro SD card $10
Download the latest OctoPi image from https://octopi.octoprint.org/
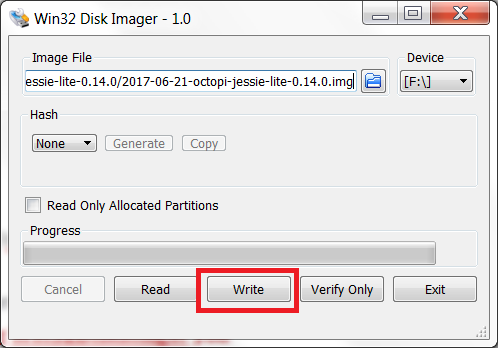
Insert your micro SD card into your computer and note the Drive letter. ***If you choose the wrong drive letter when using Win32DiskImager you overwrite and unintended disk. You’ve been warned. ***
Use Win32DiskImager to load the image onto your SD card. Select your image in the Image File drop down menu. Select your SD card drive letter from the Device drop down menu. Click Write to begin writing.
Once the write process has been completed, you will want to edit the network configuration file on the SD card so that your Raspberry Pi will know which network to connect to.
Open octopi-network.txt with Notepad++.
You will type your router’s SSID and password in the text file and remove the # symbol to allow the commands to execute.
Example of lines edited:
Before
##WPA/WPA2 secure
#iface wlan0 inet manual
#wpa-ssid "put SSID here"
#wpa-psk "put password here"
After
##WPA/WPA2 secure
iface wlan0 inet manual
wpa-ssid "MyHomeWifiName"
wpa-psk "MyHomeWifiPassword"
Save the text file.
Eject the SD card and insert it into the Raspberry Pi.
Power the RaspberryPi on.
Next you will access the Octopi webpage that is being hosted from the Raspberry Pi by typing in the ip address of the Raspberry Pi in your browser. If you do not know the ip address of your Raspberry Pi, you can check your homes router to view any newly connected devices or use a network scanning tool. You can also use the link http://octopi.local/ to access the page as well.
When you first access the Octopi, you will be prompted with questions about security. It is your option to use a user/password to access your printer. I recommend securing this if you plan on accessing your printer outside of your network through the use of port forwarding.
Printer Profile Setup – Monoprice Mini Select V2
Note: These instructions only work for the MonoPrice Mini select V2 (MPMS V2).
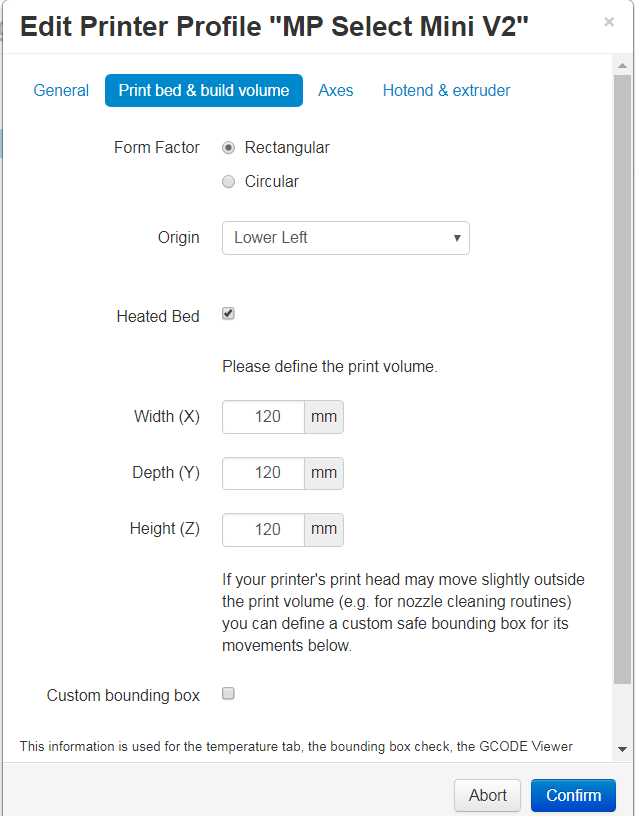
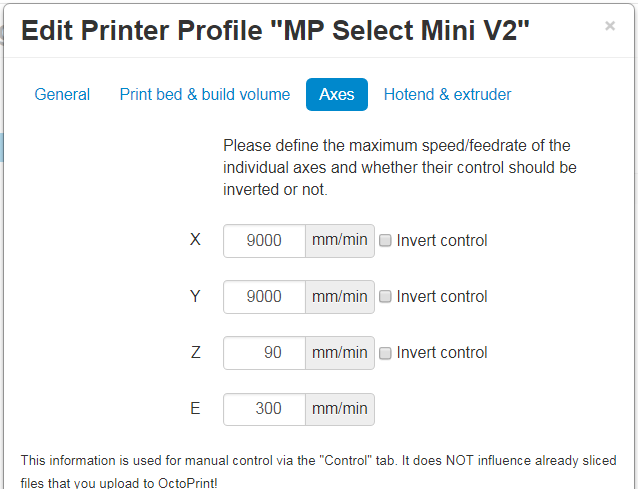
Use the printer settings below for reach of the option menus and then click “confirm” at the bottom.
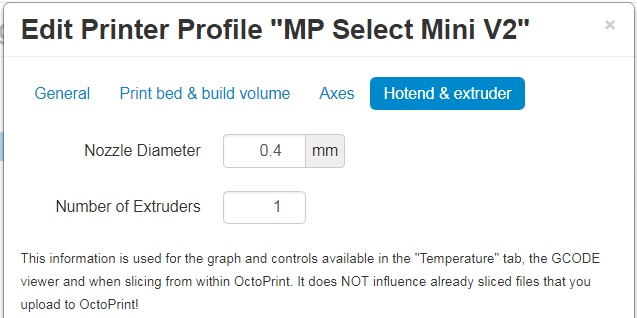
Once your printer has been setup and your Raspberry Pi has been restarted, go to the main page and select your printer from the connections tab. Select 115200 for the Baudrate. Click the connect button to connect your printer.
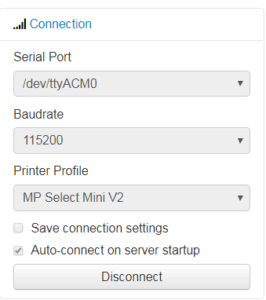
You can view that your printer has successfully connected by looking at the state of you printer on the left side of the main webpage window.
Troubleshooting
-Everything is working but the printer will not connect from the octopi webpage
Verify your printer settings are correct. There is a wrench (settings) button in the top right corner. The printer profiles can be edited here.
I sometimes have problems connected to the printer that was previously working and the connection will timeout. Click connect then immediately disconnect and connect again. I do not know why this works but it resolved my issue.
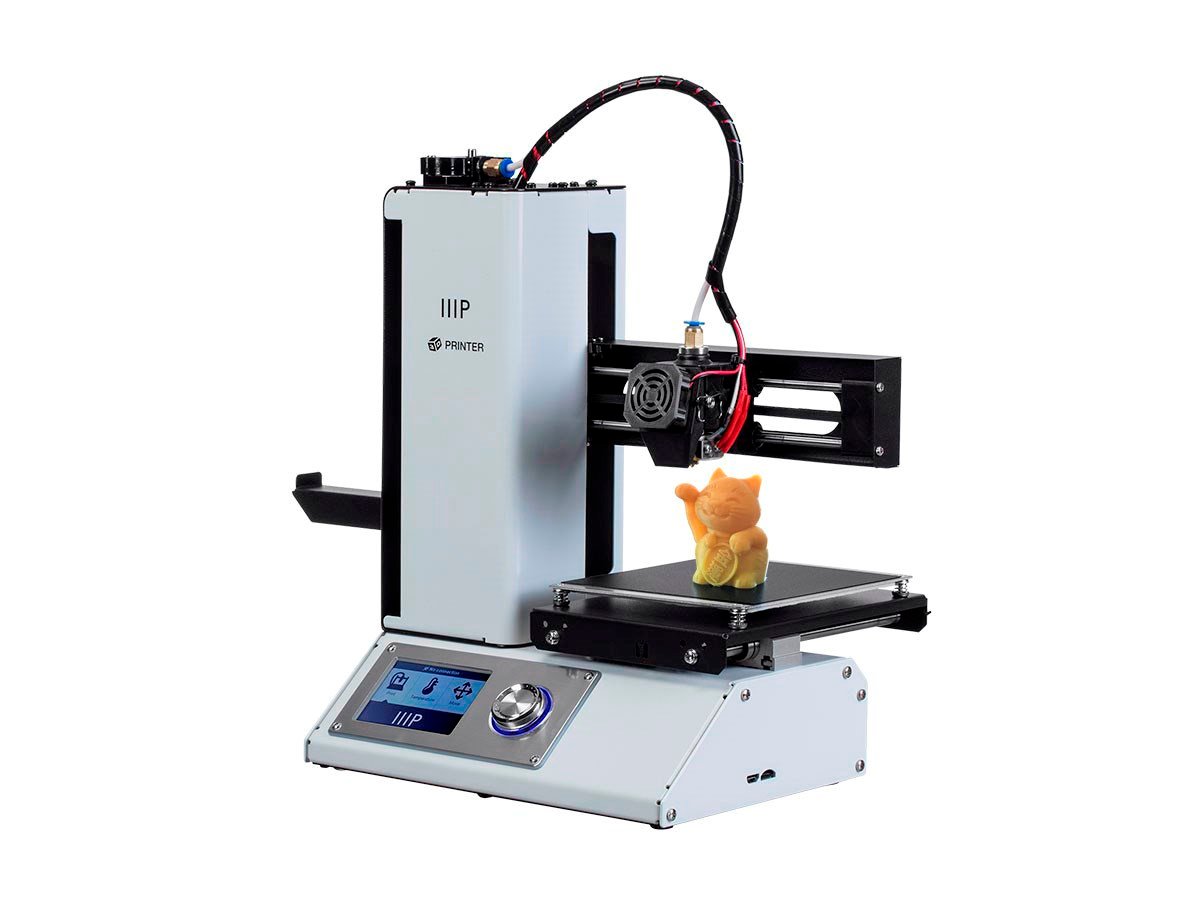
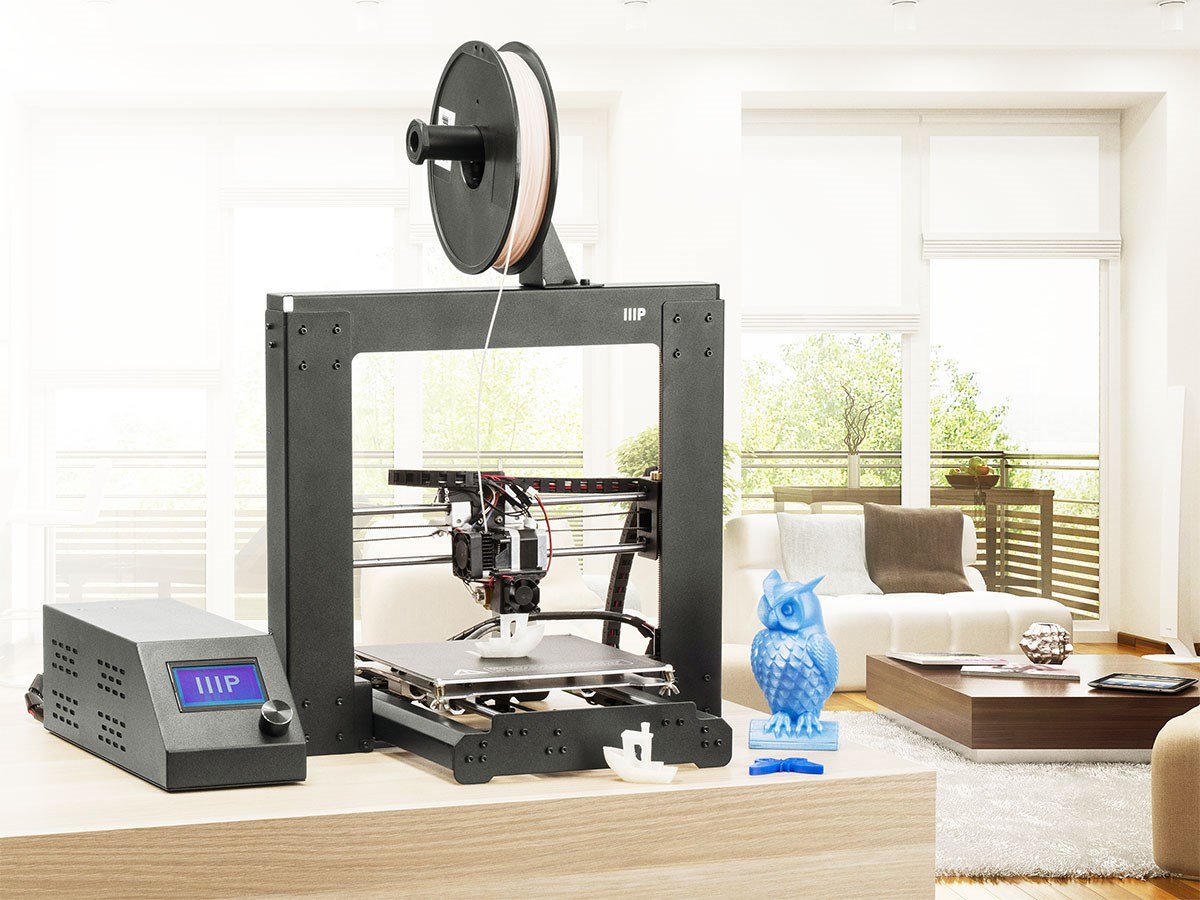



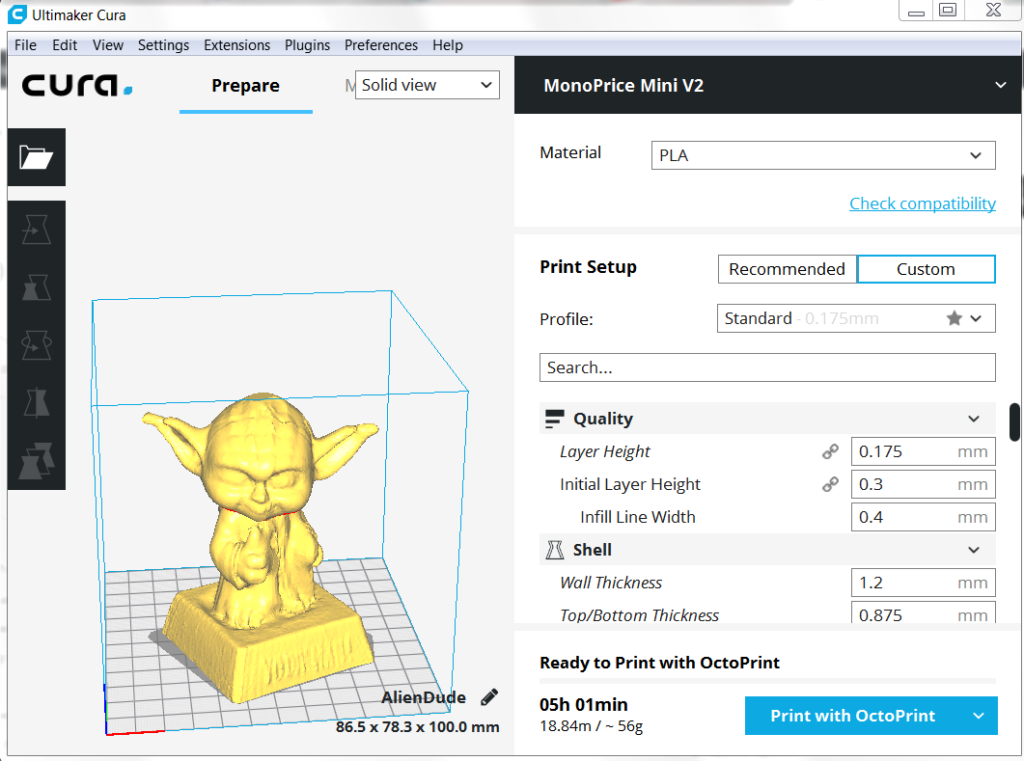
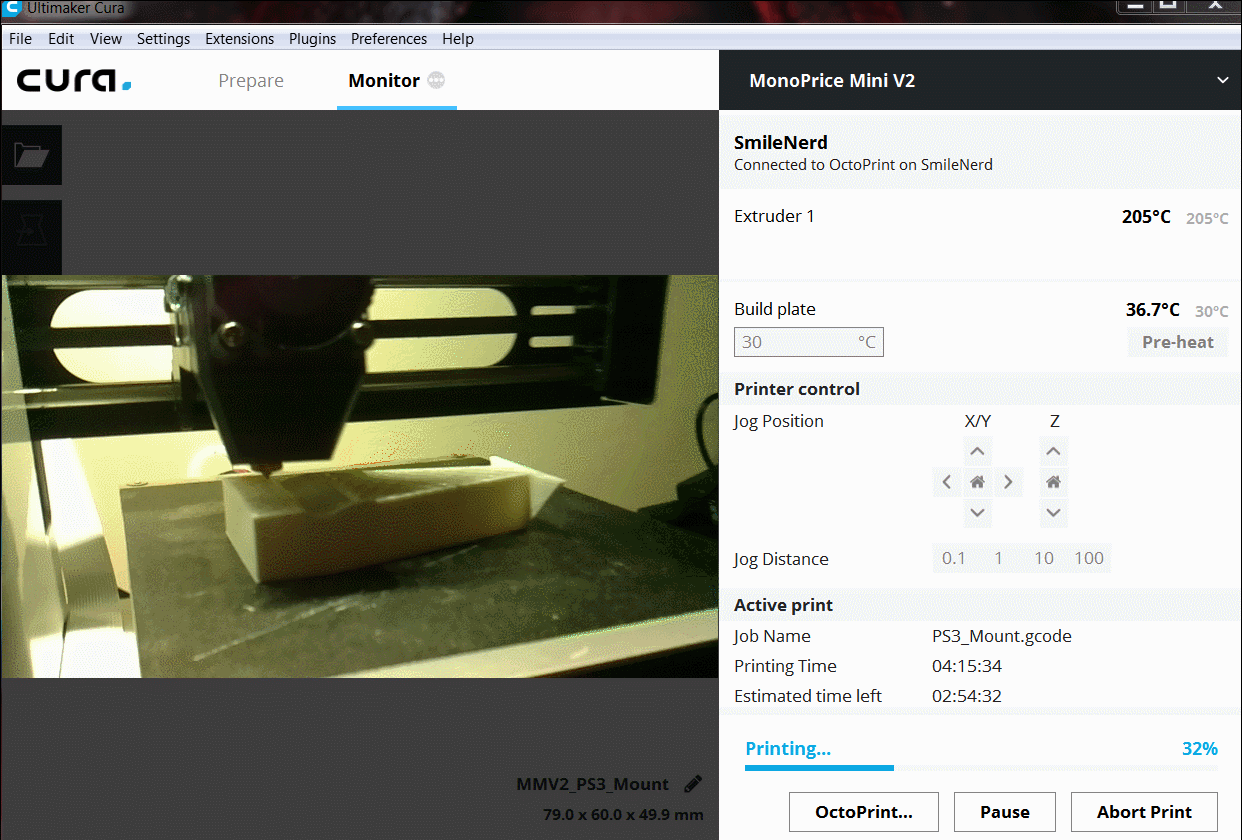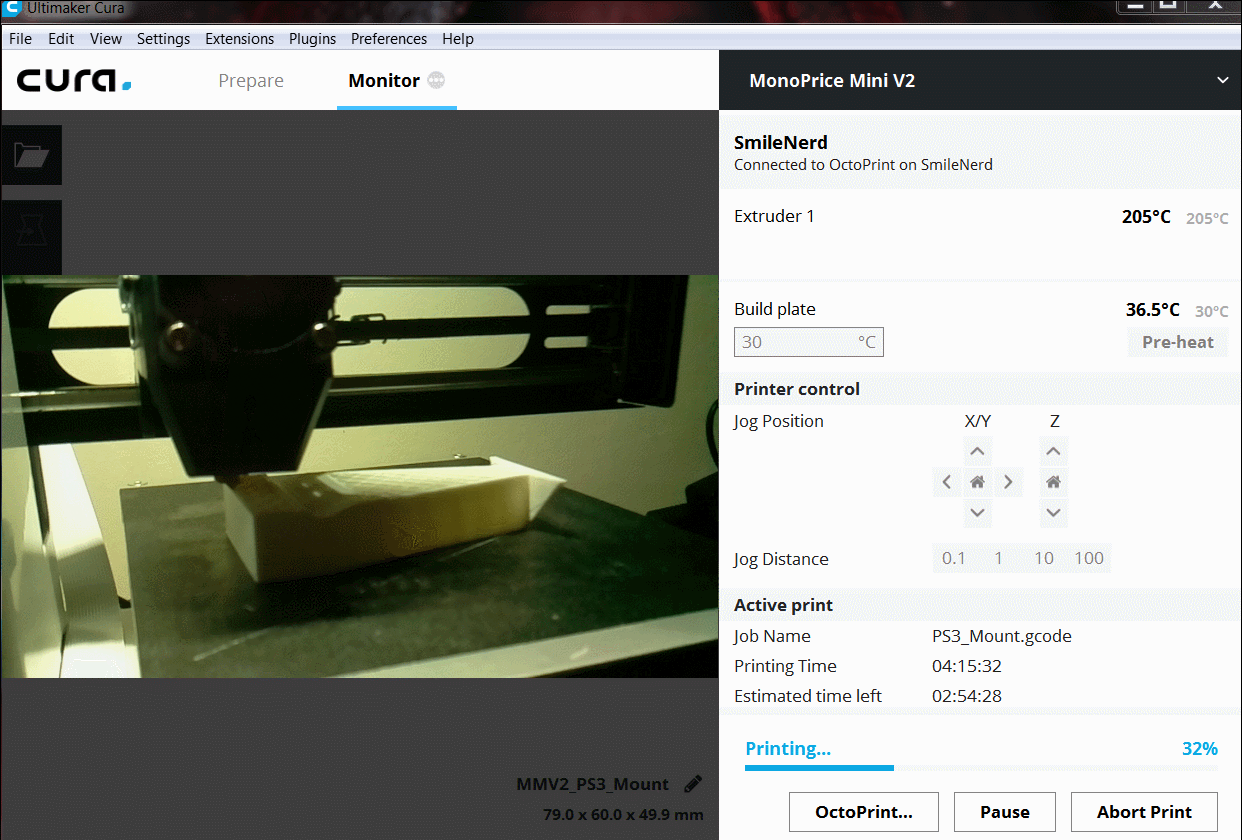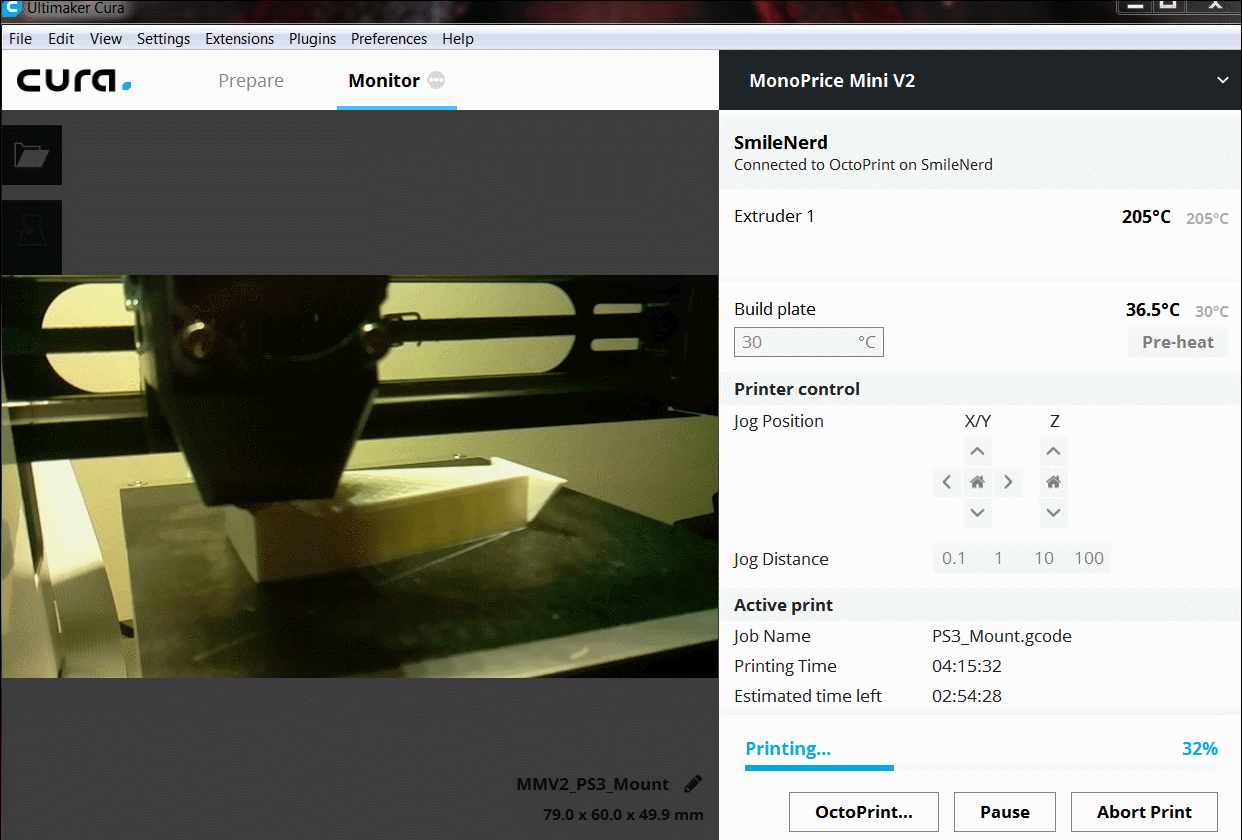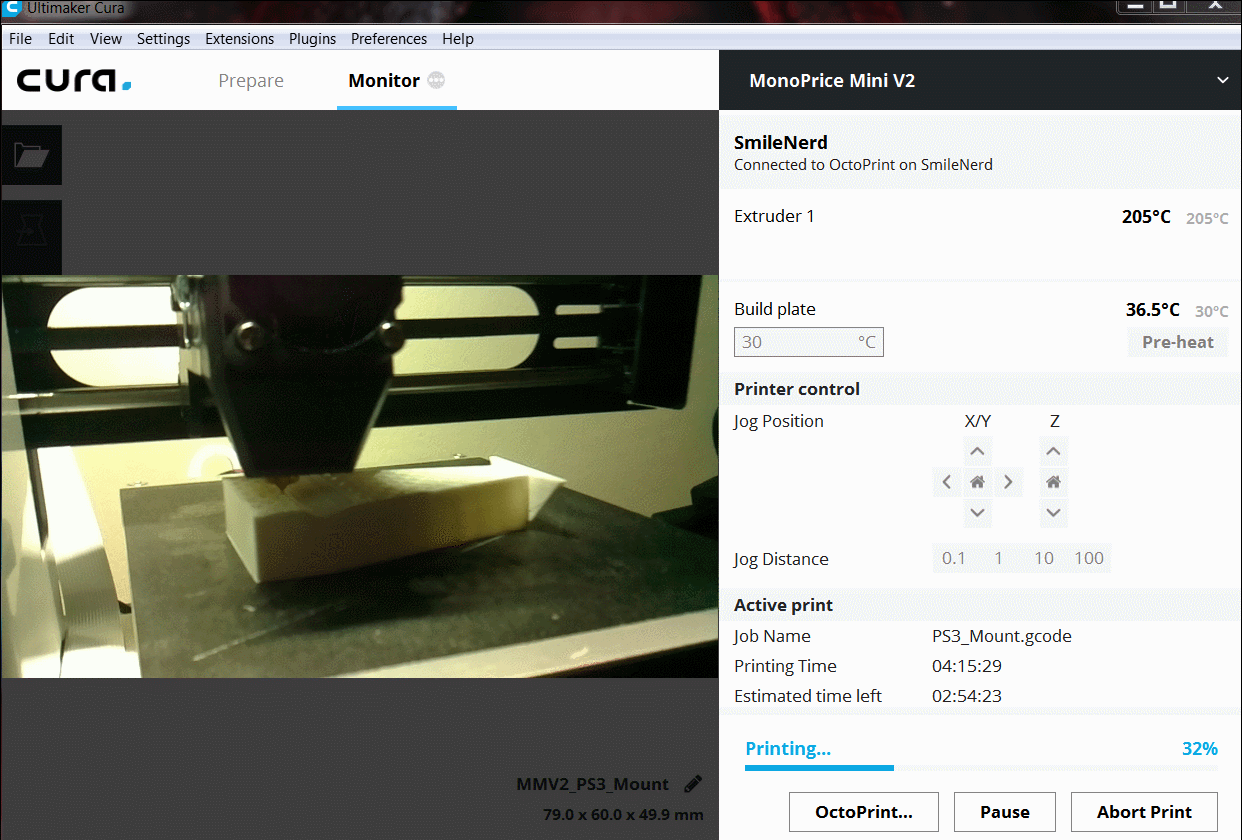



















 This is the larger version of the mini Maker select and would be my ideal choice if not for concerns with workbench space. Although it prints at the same detail as the mini it has many other advantages at around the same price. This printer has a large print bed at 7.9″ x 7.9″ x 7.1″
This is the larger version of the mini Maker select and would be my ideal choice if not for concerns with workbench space. Although it prints at the same detail as the mini it has many other advantages at around the same price. This printer has a large print bed at 7.9″ x 7.9″ x 7.1″